Sustainability has been placed on the top of the priority list of most companies due to the high impact climate change is causing on businesses associated with the growing pressure from several ecosystems such as consumers, regulatory bodies, activists, NGOs, investment groups, among others. The 2020 Leadership for the decade of action report revealed that around 92% of the C-level executives agree that sustainability must be incorporated into the business strategy for long-term success [1]. Another recent study showed that over 80% of large enterprises are very concerned specifically about the climate change agenda [2].
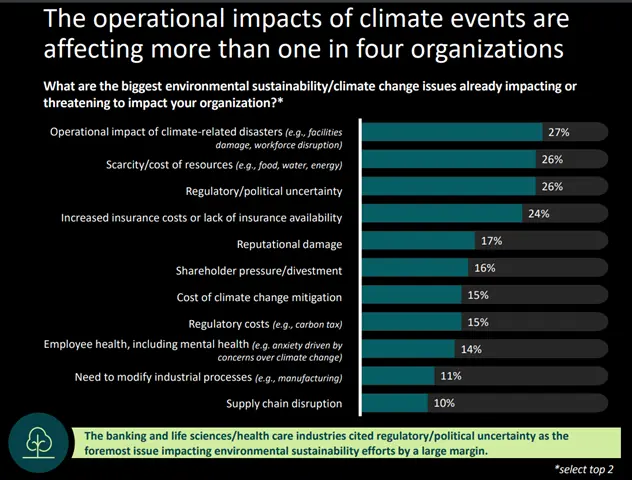
At the top of the list of key environmental challenges that affect businesses today are operational impacts related to climate disasters, cost and scarcity of resources, as well as misaligned regulations and political uncertainties across the globe. The graph from the Deloitte Global Climate survey details this list [2].
It is seen that just a few business executives and organizations are opposed to having and investing in sustainability commitments. The major challenge is to define a strategic framework to translate these commitments into viable and effective action plans and new business models, especially when there is a lack of clear and aligned targets and no standards to follow across the different value chains and regions.
Oftentimes, climate actions are built based on the principles of regional policies and typically aim to raise consumer awareness. A few examples include the efforts to decrease waste generation and proper disposal; optimization of resources during the manufacturing and shipping of goods; and the appraisal and promotion of the usage of new recycled materials, e.g., through chemical recycling. As digital transformation enables new technologies to be more integrated into new business models, organizations start to address and prioritize sustainability also in the digital dimension, a process that is still being globally shaped across different segments and thus far there is no standardized approach.
Considering this scenario, there are ethical, financial, and reputational aspects to incentivize enterprises to quickly invest and implement digital approaches to ensure more environmentally friendly solutions incorporating sustainable innovation in their new digital-based models.
The strategy of combining sustainability commitments with digital transformation, although needed and promising as an opportunity for competitive advantage, if not properly implemented, could still lead to a double-edged sword scenario.
The rapid transition to digital-empowered services is typically supported by data centers requiring infrastructures that imply high energy consumption. The IT sector alone is already a prominent contributor to this scenario, e.g., digital aspects of the aviation industry, and is estimated in this article on the green cloud to account for around 10% of global electricity demand by 2030 [3].
Concomitantly, new advancements in cloud computing and artificial intelligence (AI) are also enabling more sustainable innovation approaches. It is estimated that the efficiencies gained through cloud computing could prevent the emission of more than a billion tons of carbon dioxide in the next couple of years according to a study from the research firm IDC [4]. Although the AI algorithms applied in more recent software programs entail noteworthy training, refinement, and resources; advancements in novel computers’ design, optimized power supply systems, and more efficient hardware may powerfully lessen the digital influence on the final environmental impact [5].
The process of identification and application of digital data plays a major role in translating sustainability commitments into reachable headways. Nevertheless, it still portrays a significant challenge for most business leaders to design cohesive strategies bridging digital and green transformations.
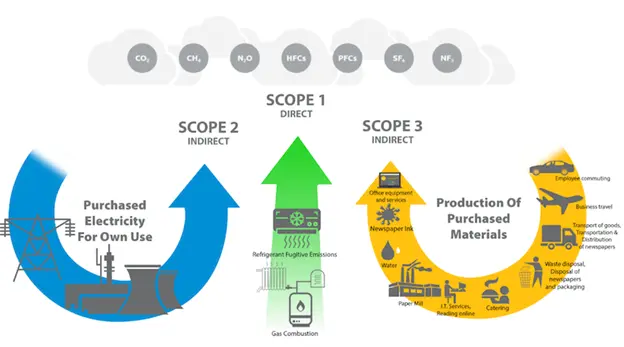
As an effect of digitalization, new technology-enabled emissions introduce additional strains as they are typically categorized as Scope 3 emissions based on the Greenhouse Gas (GHG) Protocol, i.e., those indirectly yielded by an organization throughout the inherent processes within its business, as opposed to emissions from scopes 1 and scope 2, which include those directly produced by energy consumption and own assets, as shown in the above diagram from Green Element [7].
Adopting more sustainable technology approaches can yield substantial efficiencies in the short and long term which need to be better communicated and articulated by policy-making bodies. For example, in the short term, carbon mitigation technologies can be identified and implemented to minimize environmental impact, but they alone will not be enough as discussed in this MIT Technology Review article [8].
In the medium to long term, there is room to also implement cleaner carbon-cutting or bio-based technologies, on top of the mitigation strategy, maximizing sustainable progress. Thus, there is no one-size-fits-all solution and balancing all alternatives out, in the right ratio and speed, will be key for advancing the sustainability agenda.
Putting in place a digital sustainability practice also gives enterprises the chance to lead by example, allowing them to set standards for measuring, reporting, and managing GHG Scope 3 emissions when most competitors are still at an early stage.
As much as carbon and GHG mitigation can be carried out by optimizing current processes, truly expanding the boundaries of digital sustainability will likely require new investments. With the increase of co-creation partnerships across the value chain, novel solutions are arising to enable greener and cleaner technological practices, which may provide the required means to propel advancements toward actual net-zero targets, even if businesses increasingly rely on data and energy-intensive resources to meet operational and sustainability demands.

Even before a full transition to clean energy, mitigation technologies such as carbon capture, and energy storage associated with circular economy resources strategies can be good bridges to drive the industry forward, advancing the sustainability agenda.
On top of that, digital sustainability is not only related to making the digital transformation a sustainable process, but it also implies the use of digitalization to boost progress in all sections, including reducing emissions from all 3 GHG scopes previously discussed. Thus, digital sustainability can be a powerful approach to combine the key principles and targets of the digital revolution with green transformation to effectively protect the planetary boundaries and lower environmental impact at a faster pace.
References
[1] Leadership for the decade of action report, The United Nations Global Compact and Russell Reynolds Associates – “Study on the characteristics of sustainable business leaders” (2020).
[2] Deloitte Global climate survey – “Climate Check: Business’ Views on Environmental Sustainability” (2021).
[3] Natalie Hollier, Dan Lewis-Toakley, and George Earle – “Why green cloud optimization is profitable for you and the planet” (2020).
[4] International Data Corporation (IDC) report- “Cloud Computing Could Eliminate a Billion Metric Tons of CO2 Emission Over the Next Four Years, and Possibly More, According to a New IDC Forecast” (2021).
[5] Jeremy Kahn – “A.I.’s carbon footprint is big but easy to reduce, Google researchers say” Fortune Article (2021).
[6] World Resources Institute – “Greenhouse Gas (GHG) protocol” available from: https://ghgprotocol.org/, accessed in February 2022.
[7] Green Element GHG scheme of categorization of the different emissions scopes, accessed in February 2022.
[8] MIT Technology Review article by James Temple – “Carbon removal hype is becoming a dangerous distraction” (2021).











